Most enterprise data sit in relational databases that are powerful and dependable, but not always easy to work with. Over time, complex schemas, multiple joins, and embedded business rules make it harder for people outside engineering teams to get quick answers from data.
This is where LLM SQL agents come in.
Instead of writing queries, users can simply ask questions in plain English. The agent understands the intent, translates it into SQL, and fetches the right data from the database. This removes a lot of back-and-forth, shortens analysis cycles, and helps more teams use data without waiting on technical support.
In this blog, we walk through how LLM SQL agents work, the core frameworks that power them, the real challenges teams face when deploying them, and how modern agent-based designs help turn these systems into reliable, production-ready solutions.
Jump to:
Why SQL Agents Matter in Enterprises
How an LLM SQL Agent Works (Step by Step)
SQL Agents Inside an LLM Agent Framework
Key Challenges of LLM SQL Agents
Strengthening SQL Agents with Table-Augmented Generation (TAG)
Common Use Cases for LLM SQL Agents
Why Agentic RAG Makes SQL Agents Smarter
What Is an LLM SQL Agent?
An LLM SQL agent acts as a smart layer between people and databases. It allows users to ask questions in everyday language, while the agent quietly handles the complexity of turning those questions into SQL in the background.
In practice, the process is straightforward:
- A user asks a question in plain English, just like they would in a normal conversation
- The agent understands what the user is trying to find and captures the intent
- It maps that intent to the right tables, columns, and relationships
- A SQL query is generated based on this understanding
- The query is executed in a controlled and secure way
- The results are returned in a clear, easy-to-read format so users can take action
What makes LLM SQL agents truly valuable is how they work inside real production systems. They are rarely used on their own. Instead, they operate as part of a broader LLM agent framework, working alongside other agents that provide schema context, apply business rules, and enforce access controls. This collaboration ensure responses are accurate, relevant, and safe for making data access faster and more reliable for both technical and non-technical users.
Why SQL Agents Matter in Enterprises
Most traditional BI tools work well for known questions, but they struggle when business needs change. Teams often rely on prebuilt dashboards, fixed metrics, and repeated requests to data teams just to get simple answers. Over time, this slows down decision-making and creates bottlenecks.
Business questions, however, are rarely static. They change day to day, sometimes hour to hour.
SQL agents help bridge this gap by making data access more flexible and accessible:
- They enable true self-service analytics without waiting on dashboards or reports
- Users can get answers quickly without knowing how to write SQL
- Dependence on BI and data engineering teams is reduced for everyday questions
- Data can be queried in natural language directly from live enterprise systems
This approach is especially useful for business users, customer support teams, operations, and leadership for the people who need timely answers but should not have to depend on technical teams for every query.
How an LLM SQL Agent Works (Step by Step)
A production-ready SQL agent LLM follows a clear and structured workflow to turn plain language questions into actionable data.
- Understanding the User Query
The process starts when a user asks a question in everyday language. The agent reads the query, identifies the intent, and pulls out key details like metrics, time frames, and other filters.
Example:
“What were the top five products sold last month?”
The agent breaks it down:
- Metric: top five products
- Time filter: last month
This step ensures the agent fully understands what the user wants before touching the database.
- Schema Awareness and Metadata Grounding
Next, the SQL agent in LLM uses database schema information like tables, columns, relationships, and business definitions to map the query accurately. The richer the schema metadata, the more precise the SQL that will be generated.
Semantic layers or augmented data catalogs are often used here to provide the agent with context and ensure it works with the right data.
- SQL Generation
Once the agent has context, it generates a SQL query that follows:
- The structure of the database
- Existing business logic
- Any query constraints or filters
At this stage, the output is more than just syntactically correct SQL. It is a SQL AI query that produces meaningful, actionable results aligned with the user’s intent.
- Safe Execution via SQL Agent Server
Before running the query, the SQL agent server applies safety and governance rules:
- Read-only access
- Row and cost limits to prevent heavy queries
- Role-based permissions
- PII and sensitive data masking
This ensures the SQL runs safely without exposing confidential information or overloading the database.
- Response Formatting
Finally, the data returned from the query is processed and presented in a clear, user-friendly format. Instead of raw tables, the agent summarizes or explains the results so users can quickly understand insights and take action.
This approach lets both technical and non-technical users interact with complex databases confidently, without needing to write SQL themselves, while keeping enterprise data secure and accurate.
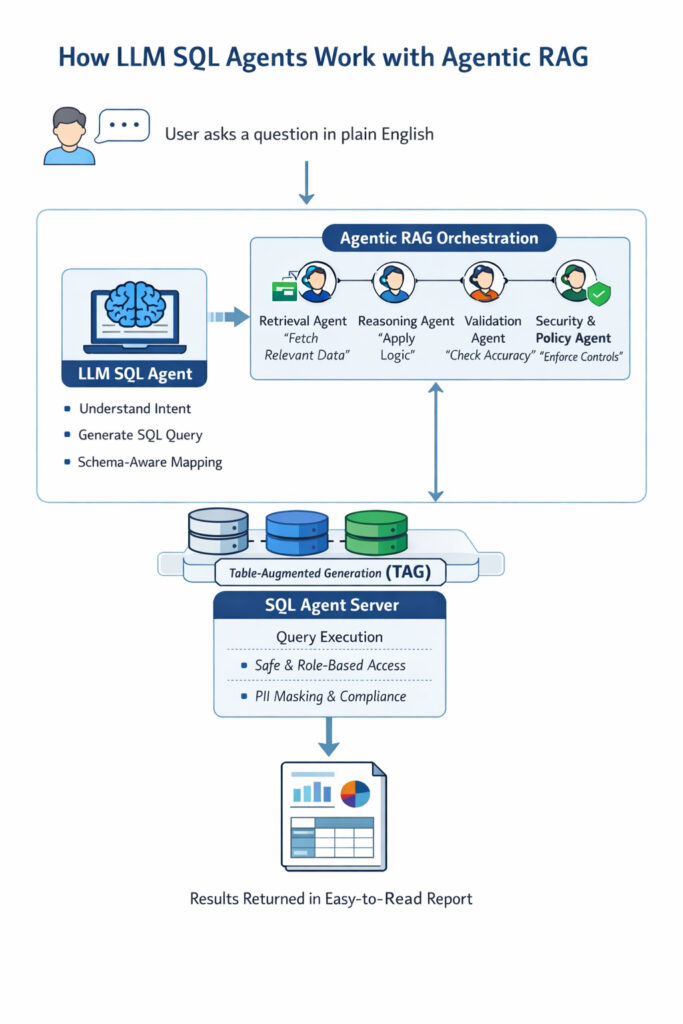
SQL Agents Inside an LLM Agent Framework
Modern LLM agent frameworks do not rely on a single model call to answer questions. Instead, multiple specialized agents work together to handle different aspects of the query.
SQL agents often collaborate with:
- Retrieval agents (RAG): Pull relevant data and context from structured or unstructured sources
- Reasoning agents (ReACT / chain-of-thought): Break complex queries into smaller steps and plan the best approach
- Validation agents: Check query accuracy and ensure results are reliable
- Security and policy agents: Enforce access controls, data masking, and compliance rules
This agent-based orchestration brings several benefits:
- Higher accuracy: Queries are more precise because multiple agents cross-check the context and logic
- Better context awareness: Agents understand the schema, business rules, and user intent more effectively
- Stronger data safety: Sensitive data is protected during query execution
- Improved scalability: The system can handle many queries across different datasets without hardcoding solutions
Instead of building a separate tool for every possible query, AI agents dynamically invoke the SQL agent only when structured data is needed. This approach keeps analytics flexible, efficient, and secure for both technical and non-technical users.
Key Challenges of LLM SQL Agents
While LLM SQL agents can make querying databases much easier, but they are not without challenges. Understanding these issues helps teams to plan better and deploy agents safely.
- Handling Complex Queries
When databases have hundreds of tables, cross-database joins, or complex business rules, even the smartest SQL agent can struggle. This can lead to incomplete or incorrect queries if the model misinterprets the relationships or logic.
- Accuracy vs. Validity
An agent might produce SQL that runs without errors but does not actually answer the question correctly. Getting the query to be semantically accurate by returning the right insights is often more difficult than just making it syntactically correct.
- Data Security and Compliance
Without proper guardrails, SQL agents could expose sensitive information, including personally identifiable data. This is particularly critical in conversational interfaces, where users can ask a wide range of questions that may inadvertently touch restricted data.
- Training Data Limitations
LLMs are only as good as the data they have learned from. If the model has not seen enough examples from a specific domain, or lacks industry-specific context, it may struggle to generate useful SQL queries for the specialized scenarios.
Strengthening SQL Agents with Table-Augmented Generation (TAG)
Table-Augmented Generation, or TAG, helps SQL agents work more effectively in complex enterprise environments. It creates a unified, query able layer by bringing together data from multiple systems.
With TAG:
- SQL agents no longer need to manually query each separate system
- Data from CRM, ERP, billing, and operations is combined into a consistent view
- LLMs can generate SQL queries that are more accurate, complete, and up to date
By unifying fragmented data sources, TAG makes SQL agents more reliable and useful for business users, analysts, and decision-makers across the organization.
Common Use Cases for LLM SQL Agents
LLM SQL agents can transform how teams’ access and work with data. Here are some practical ways they are used in enterprises:
Business Intelligence
Instead of navigating prebuilt dashboards or waiting for SQL experts, non-technical users can ask questions in plain language and get instant insights. This speeds up decision-making and empowers more people to work directly with data.
Customer Support
SQL agents can power RAG-based chatbots that quickly pull customer information, like order history, account details, or support tickets. This helps support teams respond faster and more accurately.
Automated Reporting
Users can generate reports on demand simply by describing what they need. There is no need to wait in a BI backlog or configure complex queries manually.
Data Integration & Engineering
When data is spread across multiple systems, SQL agents make exploration easier. They help teams discover relevant information, unify sources, and simplify data integration workflows, saving both time and effort.
Why Agentic RAG Makes SQL Agents Smarter
Traditional RAG approaches simply retrieve static context for queries. Agentic RAG, on the other hand, adds reasoning and planning capabilities that make SQL agents more intelligent and flexible.
With Agentic RAG:
- Agents decide which data to retrieve based on the user’s intent
- Queries can adapt dynamically as new information or context becomes available
- Prompts are refined iteratively to improve accuracy and relevance
When paired with SQL agents, Agentic RAG enables:
- Multi-step reasoning: handling complex queries that require multiple operations or joins
- Cross-system querying: accessing data across different databases or platforms seamlessly
- Real-time, trusted answers: delivering accurate insights without manual intervention
This combination forms the backbone of production-ready LLM SQL agent systems, making them reliable, scalable, and practical for enterprise use.
Introducing Agentic RAG: Making SQL Agents Smarter
Traditional AI systems often rely on static methods to fetch information. In complex enterprise environments, this approach can fall short. Agentic RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) addresses this by combining data retrieval with reasoning and planning.
Here is how it works:
- Dynamic Planning: Agents decide the best sequence of actions to answer a query.
- Context-Aware Refinement: Prompts are updated iteratively based on the situation and previous results.
- Adaptive Queries: Agents adjust their approach as new inputs or data arrive.
When paired with SQL agents, Agentic RAG can:
- Convert plain English questions into accurate SQL queries across multiple systems
- Handle multi-step reasoning for complex business questions
- Deliver real-time, reliable answers without manual intervention
Conclusion
LLM SQL agents are changing the way organizations access and use enterprise data. Instead of relying on static dashboards or waiting for data teams, users can ask questions in plain English and get reliable answers instantly.
The key to making these agents work well is building them thoughtfully:
- Ground them in accurate schema metadata
- Use agent-based workflows for reasoning and context
- Apply SQL guardrails to keep data safe
- Leverage modern LLM agent frameworks for scalability and reliability
When done right, LLM SQL agents do not just run queries they help teams to explore data faster, make better decisions, and focus on insights rather than technical complexity.
Experience the power of LLM SQL agents yourself with EzInsights AI. Start your free trial today and see how easy it is to turn plain English questions into accurate, actionable database queries.
FAQs
What is an LLM SQL Agent?
An LLM SQL agent is a large language model–powered tool that translates natural language questions into SQL queries. It lets users access and analyzes enterprise data without needing to write SQL manually.
Who can benefit from using SQL agents?
Business analysts, operations teams, customer support agents, and even executives can use SQL agents. They enable non-technical users to interact with live data directly, reducing reliance on BI or data engineering teams.
How do SQL agents ensure data security?
Production-ready SQL agents use guardrails like role-based access, PII masking, query limits, and secure execution environments. When combined with RAG and agent frameworks, they ensure sensitive data is protected while delivering accurate results.
Can SQL agents work with multiple databases?
Yes. With frameworks like Table-Augmented Generation (TAG) and Agentic RAG, SQL agents can unify data from multiple systems like CRM, ERP, billing, or operational databases so users get consistent and up-to-date answers across all sources.

Abhishek Sharma
Website Developer and SEO Specialist
Abhishek Sharma is a skilled Website Developer, UI Developer, and SEO Specialist, proficient in managing, designing, and developing websites. He excels in creating visually appealing, user-friendly interfaces while optimizing websites for superior search engine performance and online visibility.

